Acids, Bases and Salts

This is part of a series where I am explaining key scientific concepts to my nieces. I will tag these as LearningSeries. These notes are for our reference only.
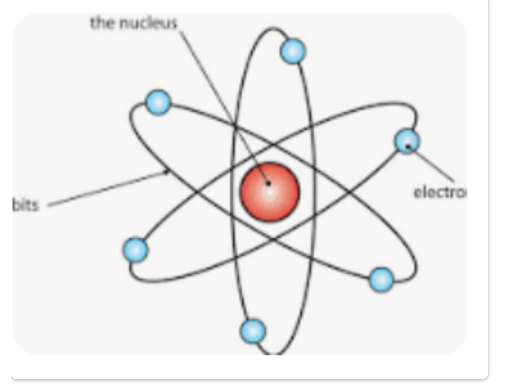
What is an atom?
An atom is the smallest particle into which an element can be divided without losing its chemical identity. Atoms consist of a heavy central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged particles called electrons. The nucleus contains positive particles (protons) and electrically neutral particles (neutrons).
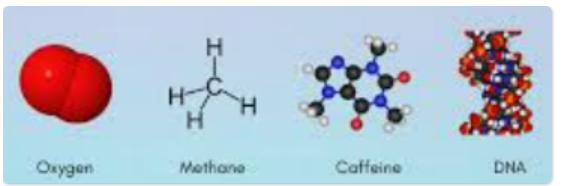
What is a molecule?
A molecule is two or more atoms connected by chemical bonds, which form the smallest unit of a substance that retains the composition and properties of that substance.
What is an ion?
An atom or a molecule that has gained or lost one or more of its parts (electrons) and so has a positive or negative electric charge. Ions can be positively charged, called cations, or negatively charged, called anions.
What is an element?
An element is a pure substance made up of only one type of atom. An element is a pure substance made up of only one type of atom. Eg- H, He, Na. All elements and their rankings (atomic number) are given in the periodic table.
What is a compound?
A compound is formed when two or more different elements chemically combine. For example, water (H2O) is a compound formed by the chemical combination of hydrogen and oxygen.
What is a mixture?
A mixture is a material made up of two or more different chemical substances which can be separated by physical method. It is an impure substance made up of 2 or more elements or compounds mechanically mixed together in any proportion.
What is an acid?
An acid is any hydrogen-containing substance that is capable of donating a proton (hydrogen ion) to another substance.
HCl -> H+ + Cl-

What is a base
A base is a molecule or ion able to accept a hydrogen ion from an acid. On dissolution in water, it ionises to form hydroxide ion as the negatively charged ion.

Types of acids and bases basis the number of Hydrogen and Hydroxide ions that they ionize into
Types of acids: Monobasic acid (1 H+, HCl), Dibasic (2H+, H2SO4), Tribasic (3H+, H3PO4)
Types of Bases: Monoacidic Base (1 OH-, NaOH), Diacidic Base (2OH-, Ca(OH)2), Triacidic Base (3OH-, Al(OH)3)
Types of acids and bases basis the amount of ionisation
Strong Acid (HCl, H2SO4,)
Weak Acid (Citric acid, Phosphoric Acid)
Strong Base (NaOH, KOH)
Weak Base (Ca(OH)2)


